Breed reproductive disorders. Due to the lack of obvious estrus symptoms in hybrid sows, if not carefully observed in dim lighting in the pens, it is easy to cause infertility due to missed mating or untimely mating. So in this case, it is best to use imported pigs and B-ultrasound to measure the follicles of sows, and then determine whether to proceed with breeding.
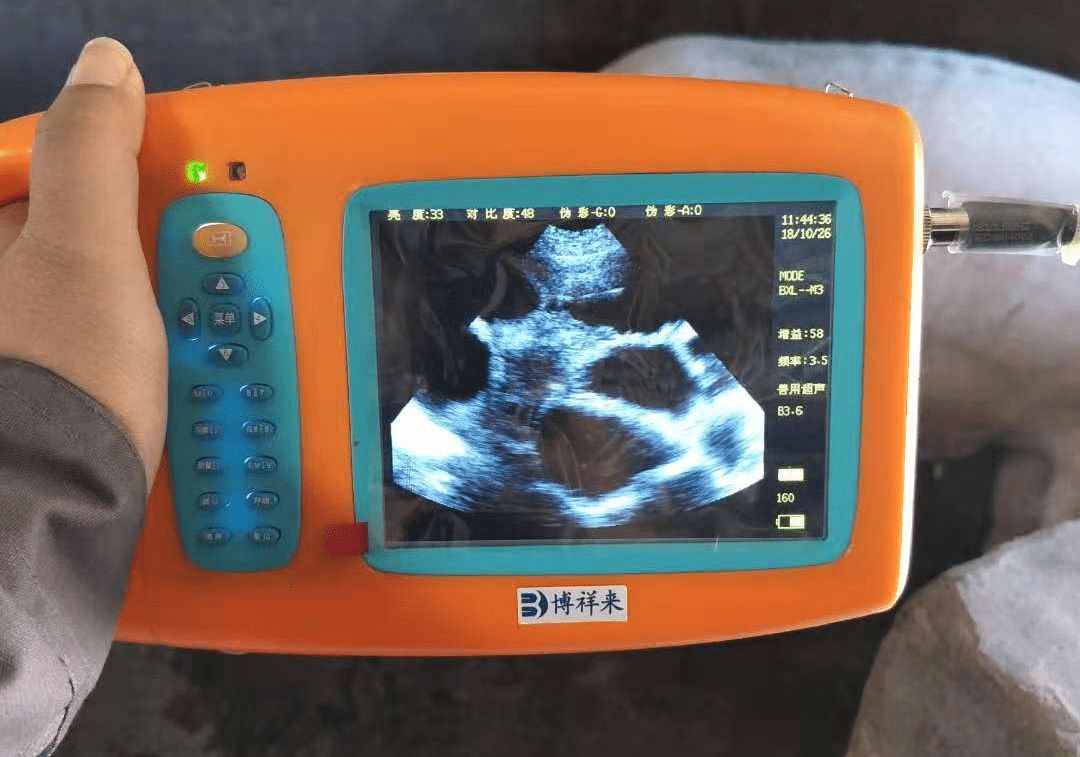
Nutritional reproductive disorders. Lean type hybrid sows have high requirements for feeding and management conditions. This survey found that 22 hybrid sows were infertile due to poor feeding management and underweight body condition, and 32 were infertile due to overweight body condition. The proportion of nutritional reproductive disorders was as high as 33.8%. It is necessary to use B-ultrasound to measure the backfat thickness of sows using Boxiang BCF imported pigs.
Disease related reproductive disorders. Diseases such as Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome, Porcine Parvovirus Disease, Porcine Pseudorabies, Porcine Japanese Encephalitis, Porcine Circovirus Disease, Porcine Epierythrocytic Disease, Porcine Brucellosis, Porcine Toxoplasma gondii Disease, etc. can all lead to infertility in sow breeding. Although no findings were found in this investigation, secondary diseases are also one of the main causes of reproductive disorders in sows. For example, poor hygiene conditions and excessive fetal size in primiparous sows can lead to damage to the uterine birth canal, resulting in endometritis, which can cause sows to not be in estrus, not be able to conceive, and even infertility in multiple pregnancies. When diagnosing these reproductive disorders, the use of ultrasound by Boxiang pigs has a significant impact.
Low parity sows have a lower mating and delivery rate. From this survey, it can be seen that 42.5% of l-3 fetuses are infertile due to unclear estrus. For hybrid sows that do not estrus for a long time after weaning, chorionic gonadotropin or anterior pituitary gonadotropin can be used to induce estrus; Strengthen the feeding and management of reserve sows in advance, neither allowing them to become overweight nor causing malnutrition; Carefully observe and master the estrus pattern of sows, pay attention to estrus identification and timely mating; Implementing repeated breeding, in addition to routine immunization, vaccine immunization should also be given as much as possible for pig reproductive and respiratory syndrome, porcine parvovirus disease, porcine pseudorabies, porcine Japanese encephalitis, porcine circovirus disease, porcine erythrocytic disease, porcine brucellosis, porcine toxoplasmosis, etc; For pigs diagnosed with secondary diseases such as endometritis on B-ultrasound, which cause non estrus, non conception, and repeated infertility in sows, treatment should be carried out.
tags: pigs and B-ultrasoundultrasoundB-ultrasound


